* 추계적 과정의 의미는? 수학적으로 일부의 결과를 가지고 전체의 결과를 예상하여 계산하는 것.
위키에서 설명하는 Renewal theory의 의미는 아래와 같다.
Renewal theory is the branch of probability theory that generalizes Poisson processes for arbitrary holding times. Applications include calculating the best strategy for replacing worn-out machinery in a factory and comparing the long-term benefits of different insurance policies.
Renewal theory는 푸아송과정을 모체로하는 확률이론의 한 분야이다. 본 이론이 쓰이는 예는, 공장에서 낡아빠진 장비의 교체 주기를 계산하거나, 전구의 수명이 다하는 것을 예상하여 아 주 긴주기에서의 교체주기를 예상하여 손이익을 계산하고자 할때 사용 될 수 있다.
Introduction
A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson process. In essence, the Poisson process is a continuous-time Markov process on the positive integers (usually starting at zero) which has independent identically distributed holding times at each integer i (exponentially distributed) before advancing (with probability 1) to the next integer:i+1. In the same informal spirit, we may define a renewal process to be the same thing, except that the holding times take on a more general distribution. (Note however that the independence and identical distribution (IID) property of the holding times is retained).
푸아송을 배울때 알게되는 Inter-arrival time 이라는 개념이 본 Renewal theory를 설명할 때 사용되었으므로 푸아송을 참고하기 바란다. Renewal theory는 holding time을 제외한 더욱 일반적인 분포라고 볼수가 있다.
Formal definition[edit]
Let  be a sequence of positive independent identically distributed random variables such that
be a sequence of positive independent identically distributed random variables such that
We refer to the random variable  as the "
as the "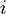 th" holding time.
th" holding time. ![\mathbb{E}[S_i]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/9/2/e/92e2d7bbd26c3eb3dfb9666dad1b61a3.png) is the expectation of
is the expectation of  .
.
Define for each n > 0 :
each  referred to as the "
referred to as the " th" jump time and the intervals
th" jump time and the intervals
being called renewal intervals.
Then the random variable  given by
given by
(where  is the indicator function) represents the number of jumps that have occurred by time t, and is called a renewal process.
is the indicator function) represents the number of jumps that have occurred by time t, and is called a renewal process.
holding times S1~Sn은 각각 IID를 따르는 Random variable을 의미하며 그 평균값은 0보다 큰 양의 값이다.
그냥 간단히 말해서, 예를들어, 푸아송 분포에서 미리 선정한 arrival rate값에 따라 사건을 발생시켰을때의 각 사건들의 발생은 서로 IID하며 그때의 사건마다 주기는 J1~ Jn까지라고 할수가 있다.
*Holding time이란? 만약 어떤 공장에서 사용하나 기계들이 존재할 때, 다른 하나의 기계가 고장나기전 하나의 기계가 고장났을때, 두 고장시간 사이의 시간간격이라고 볼 수 있다. (기계의 고장=이벤트로 볼수가 있으므로, 두 이벤트가 발생할때, 그 두 이벤트 발생시간 사이의 시간간격을 말한다.)
만약 어느 특정한 사건 n시점에서의 사건으로가서 생각해보자.
Jn은 n번째가 되기에 필요한 Si [1,n] 시간의 모든 합이라 할수있으며,
Jn에서 그 다음 사건인 n+1 사이의 interval은 [Jn,Jn+1] 이라고 정의하며, 이를 renewal intervals라고 부른다.
Random variable Xt 는 위와 같이 정의되는데, Jn이 시간 t 안에 포함된다면 그때의 최 상한선 값을 Xt라고 부르며
이를 renewal process라고 한다.
Renewal-reward processes[edit]
Let  be a sequence of IID random variables (rewards) satisfying
be a sequence of IID random variables (rewards) satisfying
Then the random variable
is called a renewal-reward process. Note that unlike the  , each
, each 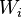 may take negative values as well as positive values.
may take negative values as well as positive values.
The random variable 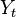 depends on two sequences: the holding times
depends on two sequences: the holding times  and the rewards
and the rewards  These two sequences need not be independent. In particular,
These two sequences need not be independent. In particular, 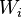 may be a function of
may be a function of  .
.
Y축 값 W1~Wn 값들은 IID 조건을 만족하며 유한할때,
이때 Random variable Yt는 1부터 Xt 까지의 모든 W값들의 합 으로 정의된다.
W는 -와 +값으로 표현이 가능하며, 이를테면 손해와 이득에 대한 표현이 가능한 변수이다.
따라서 Wi = rewards 는 시간 t에서 연속적인 cost의 losses/gains의 총합을 말한다.
'N.&C. > Probability' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Sigma Notation (Summation Notation) and Pi Notatio (0) | 2016.10.11 |
|---|---|
| [independent identically distribution] 독립 동일 분포 (0) | 2014.11.01 |
| [Markov Chain] You_tube Tutorial video. (0) | 2014.10.06 |
| [E-book] Poisson process (0) | 2014.10.06 |
| Markov chain [마코프 체인] (6) | 2013.05.09 |


![0 < \mathbb{E}[S_i] < \infty.](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/6/4/2/642646acd87e01cd6befabcb8ba03731.png)
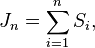
![[J_n,J_{n+1}]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/6/b/e/6bec9ae0b54f0d735f3511a0aa7f0507.png)



